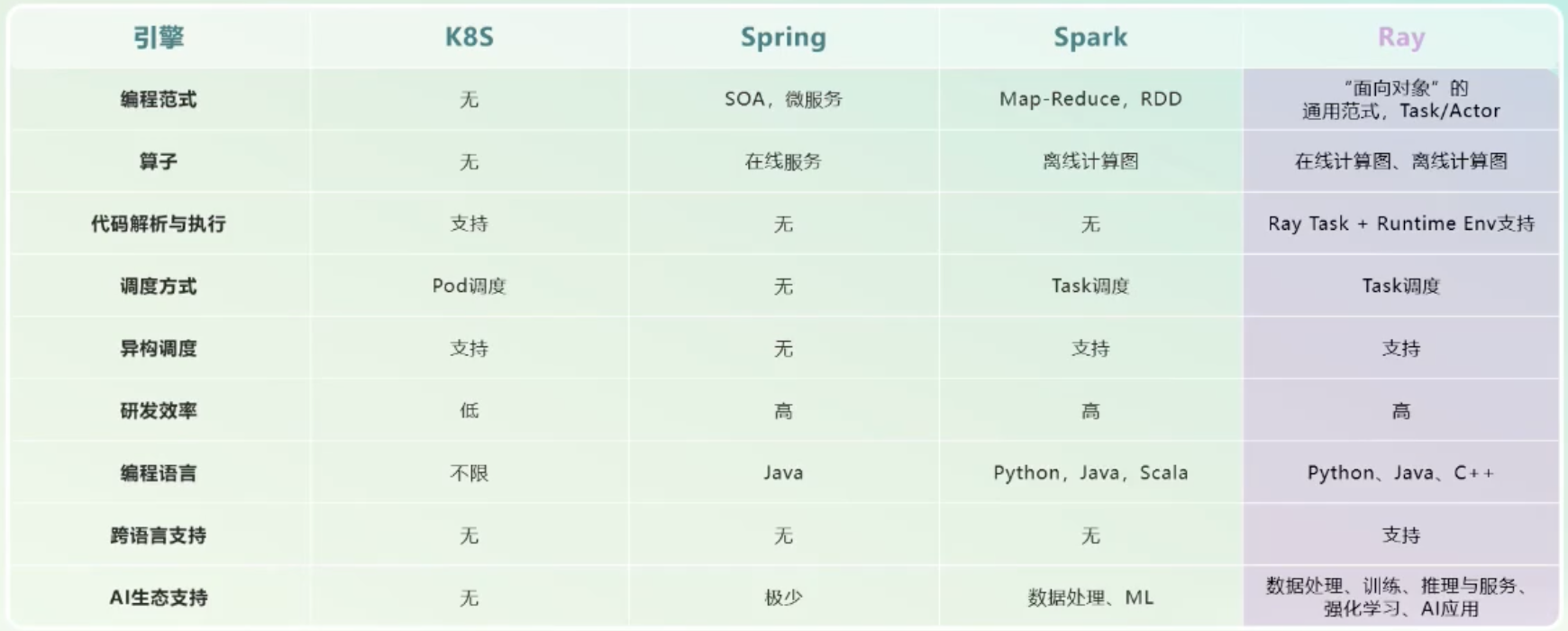
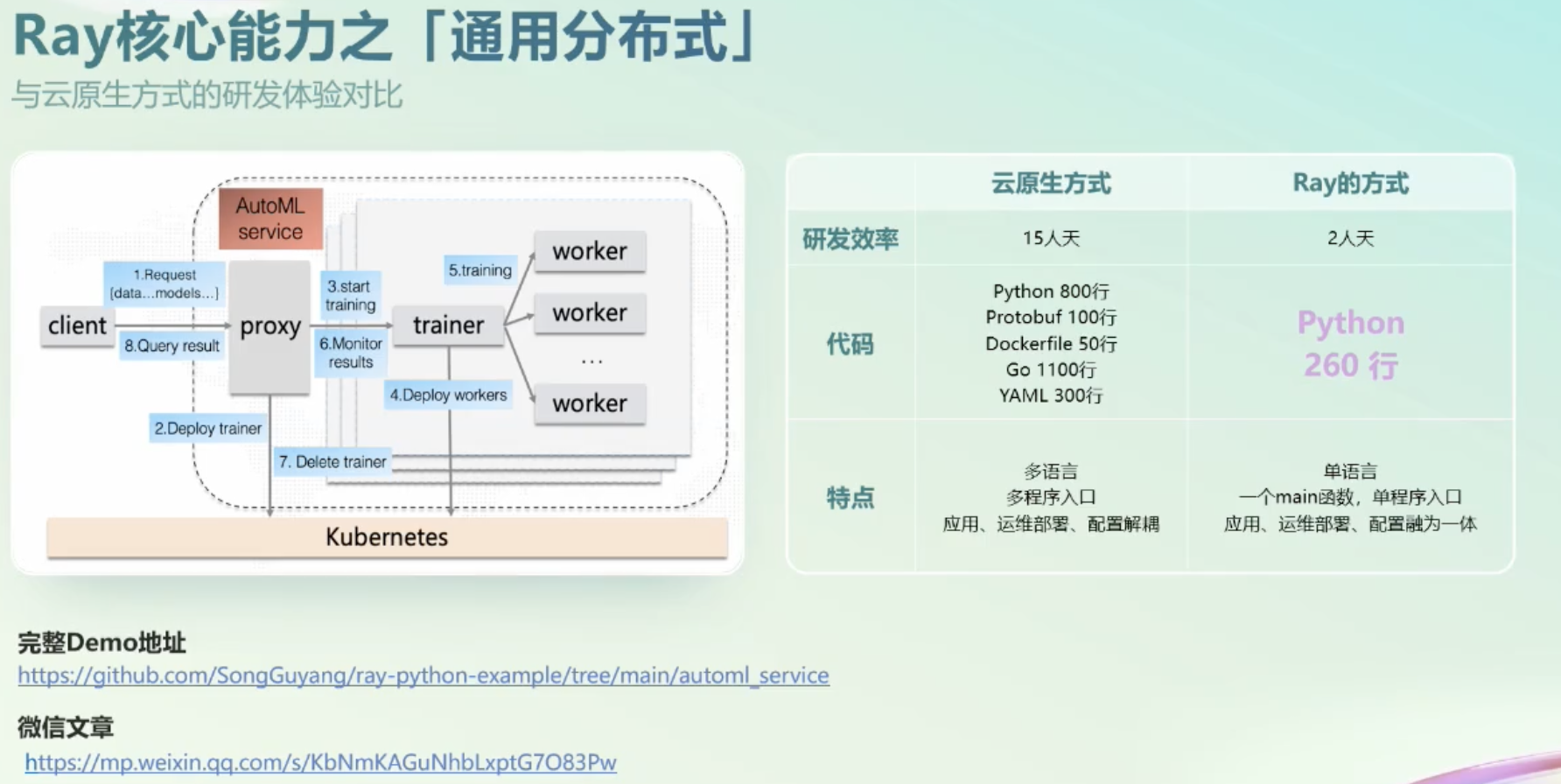
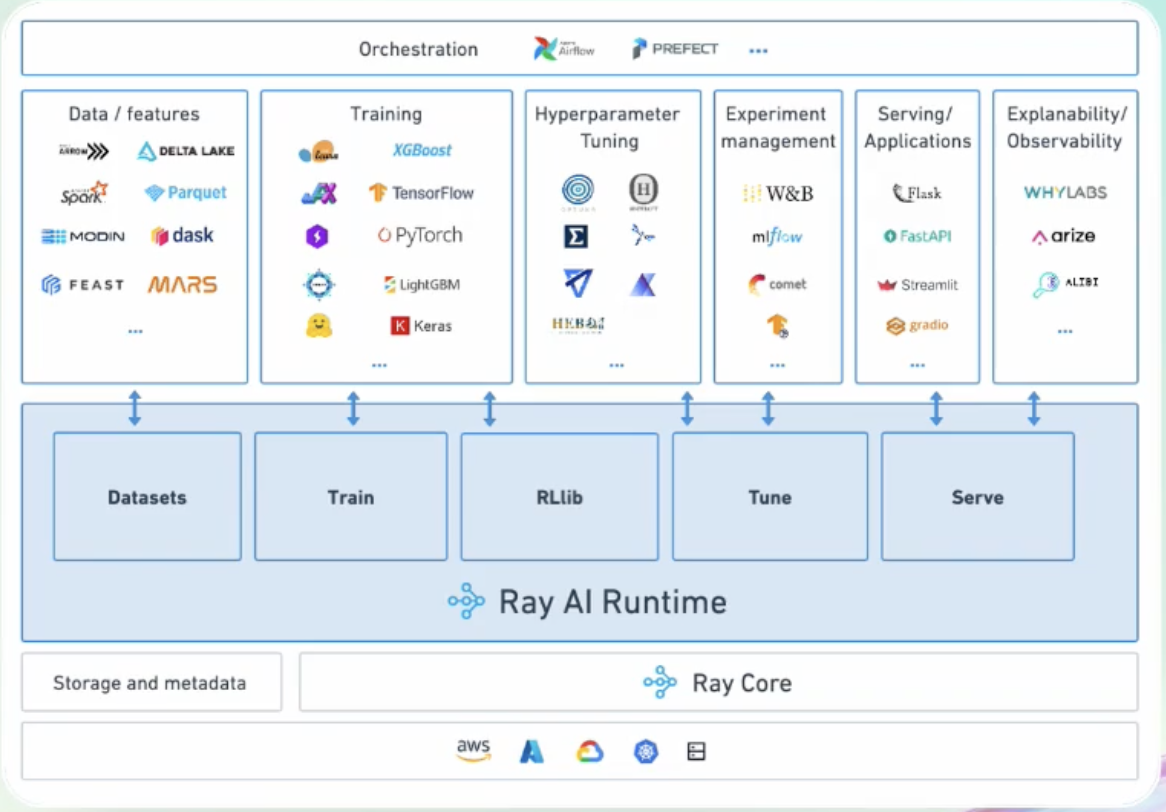
Documents
Install
pip install ray
# with client
pip install ray[client]
Architecture
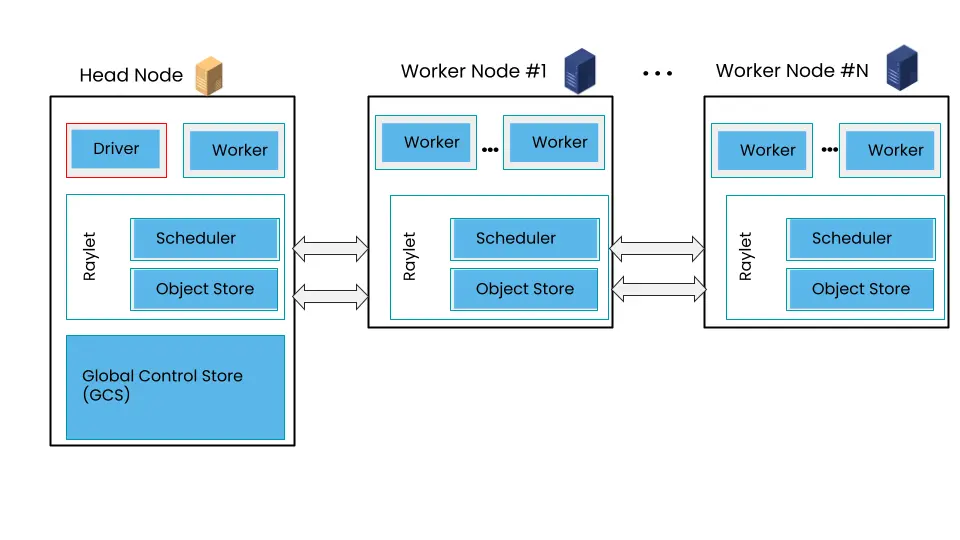
- Client Mode: Ray Client
Deploy
Kubernetes
Kuberay
Kuberay is a Kubernetes operator, it defines custom resource definitions (CRDs) for RayCluster, RayJob and RayService.
helm repo add kuberay https://ray-project.github.io/kuberay-helm/
helm repo update
# Install both CRDs and KubeRay operator v1.3.0.
helm install kuberay-operator kuberay/kuberay-operator --version 1.3.0
RayCluster
create a ray cluster
# deploy a ray cluster
helm install raycluster kuberay/ray-cluster --version 1.3.0
# check ray cluster
kubectl get rayclusters
# get pods
kubectl get pods --selector=ray.io/cluster=raycluster-kuberay
forward ray cluster ports
kubectl port-forward service/raycluster-kuberay-head-svc 10001:10001
kubectl port-forward service/raycluster-kuberay-head-svc 8265:8265
submit a ray job to the ray cluster: Quickstart using the Ray Jobs CLI
ray job submit -- python script.py --arg1=val1
# no wait for job to finish
ray job submit --no-wait --working-dir your_working_directory -- python script.py
# get logs
ray job logs raysubmit_tUAuCKubPAEXh6CW
# check status
ray job status raysubmit_tUAuCKubPAEXh6CW
# cancel job
ray job stop raysubmit_tUAuCKubPAEXh6CW
# submit to remote cluster
ray job submit --address http://remote_ip:8265 -- python script.py
# submit job with a runtime environment
ray job submit --runtime-env-json='{"pip": ["requests==2.26.0"]}' -- python script.py
cleanup
killall kubectl
kind delete cluster
Autoscaler
配置 enableInTreeAutoscaling: true, 启动 autoscaler
apiVersion: ray.io/v1
kind: RayCluster
metadata:
name: ray-cluster
spec:
enableInTreeAutoscaling: true
autoscalerOptions:
...
Worker
设置 Worker 资源
rayStartParams:
num-cpus: 4
resources: '"{\"oss\":1, \"cpfs\":1, \"nas\":1}"'
RayJob
A RayJob manages two aspects:
- A RayCluster
- A Kubernetes Job runs
ray job submitto submit a Ray job to the RayCluster
install a RayJob
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ray-project/kuberay/v1.3.0/ray-operator/config/samples/ray-job.sample.yaml
# check status
kubectl get rayjobs.ray.io
# get pods
kubectl get pods -l job-name=<rayjob_name>
# check ray job logs
kubectl logs -l job-name=<rayjob_name>
# check if the ray cluster is deleted
kubectl get raycluster
Using existing RayCluster
apiVersion: ray.io/v1
kind: RayJob
metadata:
name: rayjob-use-existing-raycluster
spec:
entrypoint: python -c "import ray; ray.init(); print(ray.cluster_resources())"
# Select an existing RayCluster called "ray-cluster-kuberay" instead of creating a new one.
clusterSelector:
ray.io/cluster: ray-cluster-kuberay
RayService
Using Ray with GPU
VMs
Commands
# 启动本地 ray 进程,可以是 head node 或 worker node
ray start
# 停止本地 ray 进程
ray stop
# 创建 ray 集群,需要提供 YAML 配置文件
ray up CLUSTER_CONFIG_FILE
# 删除 ray 集群
ray down CLUSTER_CONFIG_FILE
# execute a command on the ray cluster HEAD
ray exec CLUSTER_CONFIG_FILE CMD
# equivalent to
kubectl exec -it <raycluster_head_pod_name> -- CMD
# submit a script to the ray cluster
# The script is automatically synced to `os.path.join(“~”, os.path.basename(script))`
ray submit CLUSTER_CONFIG_FILE SCRIPT
# equivalent to
kubectl cp <script> <raycluster_head_pod_name>:~
kubectl exec -it <raycluster_head_pod_name> -- python ~/<script>
# ssh attach to the ray cluster
ray attach CLUSTER_CONFIG_FILE
# equivalent to
kubectl exec -it <raycluster_head_pod_name> -- /bin/bash
Quick Start
Init ray
import ray
# init ray
# https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/ray-core/api/doc/ray.init.html
ray.init()
# start local Ray instance
ray.init("local")
# connect to remote cluster
ray.init(address="ray://cluster_address:10001")
# show cluster resources
ray.cluster_resources()
Specifying resources
@ray.remote(num_cpus=2, num_gpus=2)
def func():
return 1
Ray Core
Task: functions can be executed asynchronously on separate Python workers.
@ray.remote
def slow_function():
time.sleep(10)
return 1
for _ in range(4):
slow_function.remote()
Actor: stateful workers. Methods called on different actors execute in parallel, and methods called on the same actor execute serially in the order you call them. Methods on the same actor share state with one another
@ray.remote
class Counter:
def __init__(self):
self.value = 0
def increment(self):
self.value += 1
return self.value
def get_counter(self):
return self.value
# Create ten Counter actors.
counters = [Counter.remote() for _ in range(10)]
# Increment each Counter once and get the results. These tasks all happen in
# parallel.
results = ray.get([c.increment.remote() for c in counters])
print(results)
# Increment the first Counter five times. These tasks are executed serially
# and share state.
results = ray.get([counters[0].increment.remote() for _ in range(5)])
print(results)
Object: remote objects are cached in Ray’s distributed shared-memory object store. Use the ray.get() method to fetch the result of a remote object from an object ref. If the current node’s object store does not contain the object, the object is downloaded.
# Put an object in Ray's object store.
y = 1
object_ref = ray.put(y)
# Get the object from the object store.
y = ray.get(object_ref)
# Get the object from task remote call
object_ref = func.remote()
y = ray.get(object_ref)
Allocate resources
@ray.remote(num_cpus=2, num_gpus=2)
def func():
return 1
ray.wait
If we use ray.get() on the results of multiple tasks we will have to wait until the last one of these tasks finishes. This can be an issue if tasks take widely different amounts of time.
start = time.time()
result_images_refs = [transform_images.remote(image) for image in SIZES]
predictions = []
# Loop until all tasks are finished
while len(result_images_refs):
done_image_refs, result_images_refs = ray.wait(result_images_refs, num_returns=1)
preds = classify_images_inc(ray.get(done_image_refs))
predictions.extend(preds)
print(f"Duration with pipelining: {round(time.time() - start, 2)} seconds; predictions: {predictions}")
Other design patterns
Environment
Environment: Ray Core - Environment Dependencies
指定 runtime_env 参数
# method 1: at ray.init
ray.init("ray://127.0.0.1:10001", runtime_env={"pip": ["requests==2.26.0"]})
# method 2: at ray.remote
@ray.remote(runtime_env={"pip": ["requests==2.26.0"]})
def func():
return 1
ray.get(func.remote())
# method 3: at ray.remote with option
ray.get(func.options(runtime_env={"pip": ["requests==2.26.0"]}).remote())
- remote 函数中使用到的本地变量
y = 768
@ray.remote
def func(x):
return x + y
# y will be sent to remote node
print(ray.get(func.remote(1)))
- 本地文件
- 方法 1:将文件打包在镜像内
- 方法 2:使用共享存储如 NAS 或者对象存储
- 方法 3:使用
runtime_env的working_dir参数
The specified local directory will automatically be pushed to the cluster nodes when
ray.init()is called.
import os
import ray
os.makedirs("/tmp/runtime_env_working_dir", exist_ok=True)
with open("/tmp/runtime_env_working_dir/hello.txt", "w") as hello_file:
hello_file.write("Hello World!")
# Specify a runtime environment for the entire Ray job
ray.init(runtime_env={"working_dir": "/tmp/runtime_env_working_dir"})
# Create a Ray task, which inherits the above runtime env.
@ray.remote
def f():
# The function will have its working directory changed to its node's
# local copy of /tmp/runtime_env_working_dir.
return open("hello.txt").read()
print(ray.get(f.remote()))
- 依赖包
- 方法 1:使用
runtime_env的pip或conda参数
import ray
import requests
# This example runs on a local machine, but you can also do
# ray.init(address=..., runtime_env=...) to connect to a cluster.
ray.init(runtime_env={"pip": ["requests"]})
@ray.remote
def reqs():
return requests.get("https://www.ray.io/").status_code
print(ray.get(reqs.remote()))
- 方法 2:使用
uv管理环境:uv + Ray: Pain-Free Python Dependencies in Clusters- 创建
pyproject.toml文件 - 使用
uv运行脚本:uv run test.py
- 创建
import emoji
import ray
@ray.remote
def f():
return emoji.emojize('Python is :thumbs_up:')
# Execute 1000 copies of f across a cluster.
print(ray.get([f.remote() for _ in range(1000)]))
Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance: Ray Core - Task Fault Tolerance
task retry
@ray.remote(
max_retries=-1, # default is 3, -1 for infinite retries
retry_exceptions=[Exception], # whether application-level errors should be retried
)
def func():
import random
if random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
raise Exception("failed")
return 1
Cancel task
obj_ref = func.remote()
ray.cancel(obj_ref)
Monitoring
# get cluster status
ray status
ray status -v
# list resources
ray list nodes
ray list jobs
ray list tasks
ray list actors
ray list objects
# list task with filters
ray list tasks --filter "state=RUNNING"
ray list tasks --filter "state=FINISHED"
ray list tasks --filter "state=FAILED"
# list task with detail
ray list tasks --detail
# get task
ray get tasks <task_id>
# print logs
ray logs task --id <task_id>
ray logs task --id <task_id> --tail 10
Ray Data
Load Data
ray.data.read_parquet("path/to/parquet")
# with ray remote args
ray.data.read_parquet("path/to/parquet", ray_remote_args={"num_cpus": 2})
Load data from arrow table
table = pq.read_table('/path/to/table')
ds = ray.data.from_arrow(table)
Load data from OSS
import ossfs
import pyarrow as pa
import pyarrow.parquet as pq
import ray
OSS_ENDPOINT = 'http://oss-cn-wulanchabu-internal.aliyuncs.com'
OSS_BUCKET = 'bucket-name'
OSS_ACCESS_KEY = '***'
OSS_ACCESS_SECRET = '***'
fs = ossfs.OSSFileSystem(endpoint=OSS_ENDPOINT, key=OSS_ACCESS_KEY, secret=OSS_ACCESS_SECRET)
# from parquet file
ds = ray.data.read_parquet(f'{OSS_BUCKET}/path/to/table', filesystem=fs)
Transform Data
def func(row):
row['new_col'] = row['col'] + 1
return row
# apply function to each row
ds.map(func)
# apply function to batch of rows
ds.map_batches(func, batch_format="pandas", batch_size=1024)
Ray Serve
Install
pip install "ray[serve]" transformers requests torch
test t5 inference
from transformers import pipeline
class Translator:
def __init__(self):
self.model = pipeline("translation_en_to_fr", model='google-t5/t5-small')
def translate(self, text: str) -> str:
model_output = self.model(text)
translation = model_output[0]["translation_text"]
return translation
translator = Translator()
translation = translator.translate("Hello world!")
print(translation)
test ray serve
from starlette.requests import Request
import ray
from ray import serve
from transformers import pipeline
@serve.deployment(num_replicas=2, ray_actor_options={"num_cpus": 0.2, "num_gpus": 0})
class Translator:
def __init__(self):
self.model = pipeline("translation_en_to_fr", model="google-t5/t5-small")
def translate(self, text: str) -> str:
model_output = self.model(text)
translation = model_output[0]["translation_text"]
async def __call__(self, http_request: Request) -> str:
english_text: str = await http_request.json()
return self.translate(english_text)
translator_app = Translator.bind()
# run serve
!serve run test_rayserve:translator_app
# test
!curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" --data '"Hello world!"' http://127.0.0.1:8000/
test llm serve
!pip install "ray[serve,llm]" vllm
from ray import serve
from ray.serve.llm import LLMConfig, build_openai_app
llm_config = LLMConfig(
model_loading_config=dict(
model_id="qwen-0.6b",
model_source="Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B",
),
deployment_config=dict(
autoscaling_config=dict(
min_replicas=1, max_replicas=1,
)
),
# Pass the desired accelerator type (e.g. A10G, L4, etc.)
accelerator_type="H100",
# You can customize the engine arguments (e.g. vLLM engine kwargs)
engine_kwargs=dict(
tensor_parallel_size=2,
),
)
app = build_openai_app({"llm_configs": [llm_config]})
serve.run(app, blocking=True)
request
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer fake-key"
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer fake-key" \
-d '{
"model": "qwen-0.6b",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
}'
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer fake-key" \
-d '{
"model": "qwen-0.6b",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}],
"chat_template_kwargs": {"enable_thinking": false}
}'
Integration
Reference